
Monocrystalline and polycrystalline silicon solar panels
With the rapid development of solar photovoltaic energy storage, its solar panel technology update iteration is also very fast, so in the selection of solar cells, usually faced with how to be able to choose the right solar cell for their projects.Brice Solar on how to choose solar cells on this issue, and combined with the current monocrystalline silicon and polycrystalline silicon batteries, together with a detailed introduction.
Monocrystalline silicon and polycrystalline silicon are the two most common solar cell materials in the photovoltaic industry, and there are obvious differences between them in terms of production process, conversion efficiency, performance characteristics and application scenarios. Below is a detailed comparison of them and how to choose the right solar cell.
1. Monocrystalline Silicon Solar Cells (Mono-Si)
Features:
High conversion efficiency: The conversion efficiency of mono-crystalline silicon solar cells is usually between 20% and 24%, and some high-efficiency products, such as TOPCon and HJT technology, have a conversion rate of more than 25%.
Excellent photoelectric performance: monocrystalline silicon has a complete crystal structure and high electron mobility, which reduces electron compounding and improves photoelectric conversion efficiency.
Low attenuation: monocrystalline silicon has stable performance, low light attenuation, and can still maintain more than 80% power generation capacity after 25 years.
Appearance: monocrystalline silicon cells are usually black or dark blue in color, with a more aesthetically pleasing appearance, suitable for BIPV.
Higher manufacturing cost: The production process of monocrystalline silicon is more complicated, requiring precision cutting and high-purity silicon materials, resulting in higher costs.
Applicable scenes:
Suitable for places that occupy little space but require efficient power generation, such as residential and commercial rooftop PV systems.
For scenes with high aesthetic requirements, such as curtain wall PV and other high-end BIPV projects.
For PV power stations with high efficiency requirements, such as PV + energy storage, distributed PV and other projects.
2. Polycrystalline Silicon Solar Cells (Poly-Si)
Features:
Lower cost:Because the manufacturing process of polycrystalline silicon is simpler and does not require single crystal drawing, the material utilization rate is high and the production cost is lower.
Mature production process:polycrystalline silicon technology has been developed for many years, with a stable manufacturing process and large production capacity.
Better heat resistance:in a high-temperature environment, some polycrystalline silicon components have a smaller decline in performance.
Lower conversion efficiency:polysilicon conversion efficiency is generally 16% to 19%, lower than monocrystalline silicon.
Larger light decay:polysilicon material has more internal grain boundaries and a higher electron complex rate, so the long-term light decay is faster.
Uneven appearance:the color of polycrystalline silicon cells is usually blue or dark blue, and there is obvious texture between grains, which is not as beautiful as monocrystalline silicon.
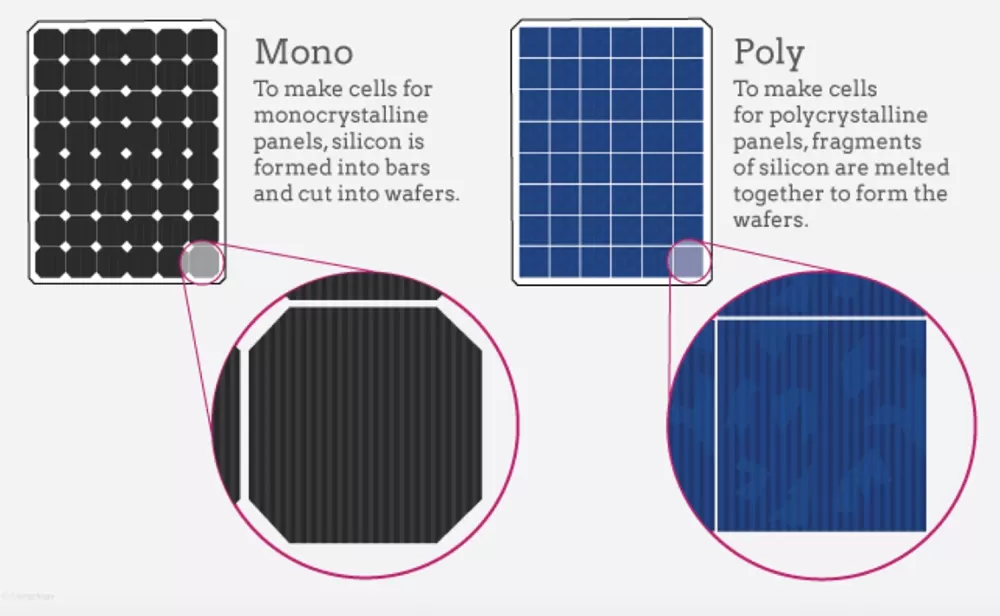
Monocrystalline and polycrystalline silicon appearance show
Applicable scenes:
Applicable to scenes with sufficient area and strict cost control, such as large ground-based PV power stations.
Cost-sensitive but not high efficiency requirements of the roof, such as commercial and industrial photovoltaic projects.
Also applies to high temperature environment projects, such as part of the temperature coefficient of polycrystalline components better place.
3. monocrystalline vs polycrystalline
|
Parameter |
Mono-Silicon (Mono-Si) |
Polysilicon (Poly-Si) |
|
Conversion efficiency |
20% to 24% (high efficiency) |
16% to 19% (lower) |
|
Appearance |
Rounded corners, no pattern on the surface |
Right angles at corners, lattice pattern on surface |
|
Color |
Black/dark blue, uniform and beautiful |
Color/dark blue, uneven |
|
Production Cost |
Higher |
Lower |
|
Power Output |
Higher |
Lower |
|
Light Attenuation |
Lower |
Relatively high |
|
Temperature Coefficient |
Slightly higher (slightly less high temperature performance) |
Lower (better adapted to high temperatures) |
|
Durability |
Tempered glass encapsulation is more weather resistant |
Satisfies common scenario needs |
|
Applicable Scene |
High efficiency PV systems, residential, commercial rooftops, BIPVs |
Large ground power plants, cost-sensitive projects |
|
Lifetime |
Up to 25 years |
About 15-20 years |
4. How to choose?
How to choose monocrystalline or polycrystalline silicon needs to be considered according to budget, space, efficiency requirements, installation environment and other factors:
Suitable for monocrystalline silicon
Limited space, need to maximize power generation, such as residential roofs, commercial roofs, BIPV projects.
Need high efficiency and stable system, more than 25 years of long-term investment projects, sensitive to light attenuation applications.
High aesthetic requirements, e.g. building curtain wall, PV glass roof, etc.
Projects with relatively sufficient budget, can accept higher initial investment but better long-term return.
Situations suitable for choosing polysilicon
PV projects with limited budget, large-scale PV power stations, industrial and commercial roofs that need to control costs.
The installation area of solar panels is large and not affected by efficiency, such as agricultural photovoltaic, desert photovoltaic power plants.
Relatively high-temperature environments, such as some hot areas, due to the temperature coefficient of some polycrystalline modules is better.
Need for short-term return on investment projects, due to the initial investment is small, short payback period of the commercialization of photovoltaic applications.
5.Monocrystalline silicon and polycrystalline silicon development trend

Monocrystalline silicon solar panels
Monocrystalline silicon will gradually replace polycrystalline silicon, monocrystalline silicon market share has exceeded 90%, due to the development of new technologies such as PERC, TOPCon, HJT, monocrystalline silicon cost continues to decrease, efficiency improvement is obvious.
Polycrystalline silicon market under the slowly shrinking, with the monocrystalline silicon production cost reduction, polycrystalline silicon market share is gradually reduced, applicable to specific low-cost projects.
With the rise of N-type monocrystalline technology, such as TOPCon, HJT (heterojunction) and other new N-type monocrystalline silicon technology, with higher efficiency, lower light decay, is an important direction for future PV technology.
6.Comprehensive recommendations
Home users
If the budget is sufficient and there is enough sunshine, choose monocrystalline silicon to get higher power generation revenue; if the budget is limited or there are more cloudy and rainy days, polycrystalline silicon is more cost-effective.
Commercial and industrial users
Prioritize monocrystalline silicon because its high efficiency and long life can reduce the whole life cycle cost, especially suitable for high electricity price areas.
Public facilities and agriculture
Polycrystalline silicon is suitable for schools, hospitals and other scenarios that require stable power supply and general lighting conditions, or agricultural greenhouses that combine power generation and light transmission needs.
Combining the above three scenario projects and by combining light conditions, budget, installation scenarios and long-term needs, you can maximize the economic and environmental benefits of your PV system by choosing the right solar panels for your own project.









One step to find us,we will respond within 24 hours.
More Contact Details
008613738639386
[email protected]