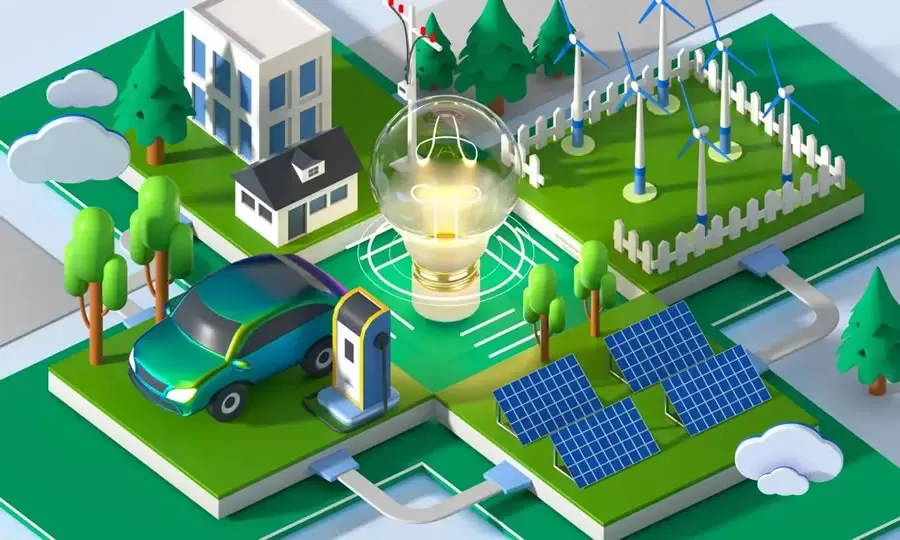

Against the backdrop of accelerating global energy transition and the continuous development of renewable energy technologies, the combination of home photovoltaic (PV) systems and smart microgrids is seen as a core scenario for low-carbon living in the future, and more and more households are beginning to realize that PV systems can provide clean, sustainable energy. However, there are still a lot of misunderstandings in this field, there are some misunderstandings and rumors about home PV systems and microgrids are circulating, and even rumors hinder the public's cognition and decision-making.Brice Solar combines the industry's cutting-edge technology with real cases to break down the common misunderstandings one by one and restore the truth.
Rumor 1: “The cost of home PV system is too high, ordinary people can't afford it.”
Truth: Technology iteration + policy support, home PV has entered the era of universal benefits
Over the past decade, according to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), the price of PV modules has dropped by more than 80%, and the popularization of high-efficiency modules (e.g. TOPCon, HJT) has further reduced the unit cost of power generation. In China, for example, the initial investment for a 5kW home PV system (including energy storage) is about 30,000-50,000 RMB, and combined with the “self-generation and self-consumption+grid access” model, most families can pay back their capital in 6-8 years.
Case: In China and Germany, many companies have launched “PV + storage” leasing services, users do not need to invest in the first stage, by paying a fixed monthly fee to enjoy clean electricity, annual savings of up to 40% of the electricity bill.
Rumor 2: “PV power generation is unstable, rainy days/nights can not be used”.
Truth: Intelligent microgrid + energy storage technology guarantees all-weather power supply.
Modern home energy systems have formed a closed loop of “photovoltaic + energy storage + intelligent control”. Tesla Powerwall, Huawei's home green power program as a representative of the energy storage equipment, can be excess power storage during the day and released at night; smart microgrids can automatically switch between utility power and photovoltaic power supply, combined with AI prediction of the weather to adjust the charging and discharging strategy.
Case in point: the “virtual power plant” project in Victoria, Australia, which successfully copes with the risk of power outages caused by extreme weather by aggregating the PV and energy storage equipment of thousands of households and unifying the scheduling of the grid during peak hours.
Rumor 3: “Installing a PV system will damage the roof and make maintenance troublesome later on.”
Truth: Lightweight design and intelligent operation and maintenance have already solved the hidden danger.
Currently, PV modules are made of lightweight materials (weight of a single module <20kg) and hole-free installation technology, which requires very little load-bearing on the roof. In addition, intelligent monitoring platforms (e.g., iSolarCloud) can detect system status in real time, with automatic alarms for faults, reducing operation and maintenance costs by 70% compared to a decade ago.
Case: Panasonic Japan launched the “photovoltaic tile” integrated program, directly embedded PV panels in the roof building materials, both waterproof, wind-resistant features, service life of more than 25 years.
Rumor 4: “Photovoltaic panel production is polluting, belonging to the ‘false environmental protection’.”
Truth: Low-carbon process + recycling technology realizes the greening of the whole life cycle
Global leading companies have realized 100% green power supply for PV silicon production, and the carbon footprint per unit of power generation is 95% lower than that of coal power. Data from China Photovoltaic Industry Association shows that the recycling rate of crystalline silicon modules exceeds 90%, and the EU's “Circular Solar” program requires 100% recycling of modules by 2030.
Case: First Solar's CdTe thin-film module adopts closed-loop recycling technology, and 95% of semiconductor materials and 90% of glass can be recycled for each MW module.
Rumor 5: “Smart microgrid is a ‘niche experiment’, the technology is not yet mature”
Truth: Global scale application has verified its economy and reliability
Smart microgrids have been landed at the community level and even city level through technologies such as energy routers and blockchain metering. According to Bloomberg New Energy Finance, the global installed capacity of microgrid will exceed 30GW in 2023, with industrial and commercial parks and island communities becoming the mainstream application scenarios.
Case: Huzhou, Zhejiang Province, China, “Zero Carbon Smart Park” project, integrating photovoltaic, energy storage, charging piles and energy management platform, realizing 100% green power coverage and annual carbon reduction of 12,000 tons.
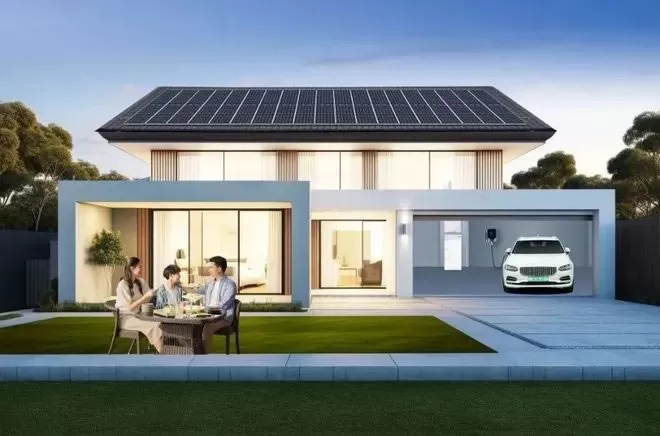

Conclusion: Embrace the trend and make rational decisions
Although home photovoltaic and smart microgrid technologies are rapidly evolving and show great potential, there are still some misconceptions and rumors in the market. Home photovoltaics and smart microgrids are not “future concepts” but accessible solutions for low-carbon living today. By eliminating misconceptions and utilizing policy dividends, such as net metering tariffs and tax breaks in various countries, home energy systems will become a long-term investment with both economic and environmental value.
As solar PV technology continues to advance, home PV systems and smart microgrids will become an important part of home energy management in the future, bringing a cleaner, smarter, and more economical electricity experience to every family.








One step to find us,we will respond within 24 hours.
More Contact Details
008613738639386
[email protected]